One of the first things you’ll need if you want to build an online presence is a domain name. But how do domain registrations operate and what takes place throughout a domain name’s lifecycle? we’ll explain everything to you, along with some insights into domain name registration and Singapore web hosting services.
Unlocking the mystery: why a domain owner needs to understand the life cycle of a domain name
A thorough understanding of the domain name life cycle is crucial for business owners. Across all top-level domains (TLDs), millions of domain names are registered, renewed, or expire each year. This is because every domain name goes through a natural life cycle, and comprehending this process is critical for anyone responsible for managing their organization’s domain names. In Singapore, where web hosting services are a thriving industry, understanding the domain name life cycle can provide an edge in managing your online presence.
Exploring the life cycle of a domain name: understanding its various stages
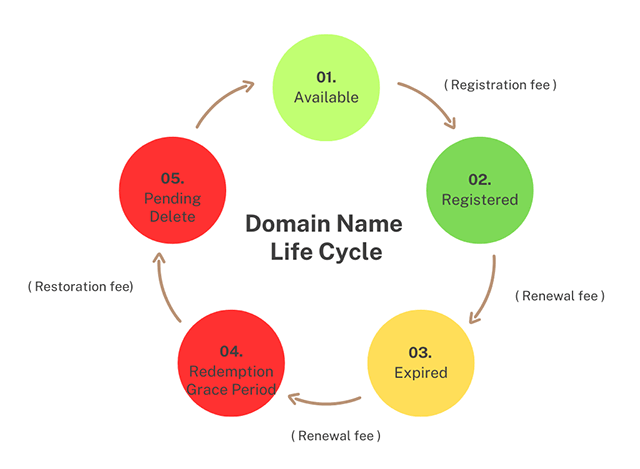
A domain name can often be in one of five various statuses, including:
- Available for registration
- Registered
- Expired
- Redemption Grace Period
- Pending Delete
Available for registration
In the first phase of a domain name’s life cycle, it is available for registration, which means that anybody can register it as long as they abide by the policies of the relevant domain extension. While some domain extensions provide worldwide registration, others might have particular criteria that must be satisfied. Domain name registration in Singapore can be done through local web hosting companies or international providers, depending on your preference.
In this phase, interested parties can use any reputable domain name service provider to register a domain name. Online domain name registration is possible, and the duration of the registration can range from one to ten years, depending on the provider.
The selection of the appropriate domain name can significantly affect your online presence at this crucial stage in creating a digital identity for your brand. It’s crucial to choose a name that fits your brand, is memorable, and is simple to spell. If you’re targeting a local audience in Singapore, consider registering a domain name with a .sg extension to establish a strong local identity.
Registered
Once registered, a domain name is no longer available for registration by any other organization. The domain name can now be actively used for online services like hosting websites or emails. The domain name is regarded as “parked” for potential usage if it is not already being used.
A domain name may be parked for a number of causes. One justification is to prevent others from stealing a valuable domain name. Another rationale is to utilize the secondary domain as an alias to drive users to the parent domain’s website. A parked domain name can also be used to keep a domain name in reserve before selling it to a potential buyer.
While a domain name’s active status is essential for businesses, the parked status can offer important protection and flexibility. It’s vital to remember that the domain name may not be bringing in money or traffic while it is in the “parked” status. As a result, it’s critical to compare the objectives of your company to the advantages and disadvantages of the parked status.
Expired
Every domain has an expiration date that may be easily found by looking up the WHOIS information. The domain owner is usually reminded well in advance of the expiration by domain name service providers, who send notices 60 to 30 days beforehand. The domain will go to an expired state if the owner forgets to renew it before the due date.
Visitors attempting to access a site through their web browsers will see a warning saying “This site can’t be accessible” once the domain has expired. This is because the domain is no longer resolvable and has been taken from the nameservers. But, depending on the provider’s policies, the domain owner still has an opportunity to reclaim it within a renewal grace period of 30 to 45 days. Although there are potential risks, they can renew the domain at the standard cost.
The greatest danger is that, following expiration, the domain name service provider might actually transfer the domain directly to another party. Furthermore, after 3 to 5 days of expiration, the majority of providers begin parking the domains, which may result in the display of adverts, announcements of domain auctions, or invitations to interested parties to indicate their desire to buy the domain.
Redemption Grace Period
The domain enters a redemption grace period if the owner of the domain does not renew it even after the expiry renewal grace period has passed. Only the previous registrant can renew the domain during this phase, which typically lasts for 45 days and is associated with a higher cost. For domains with this status, the WHOIS record will show “Redemption Period” as the domain status. Restoring a domain name at this stage can cost up to 5 to 15 times the renewal cost.
Pending Delete
A domain enters the pending delete status when its redemption grace period has expired. The domain can no longer be renewed at this time, and it will be removed after a predetermined amount of time. After that, the domain name enters the domain name life cycle once more and is once more open for registration.